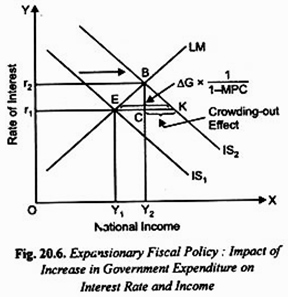
Let us first explain how IS-LM model shows the effect of expansionary fiscal policy of increase in Government expenditure on level of national income.
This is illustrated in Fig. 20.6. Increase in Government expenditure which is of autonomous nature raises aggregate demand for goods and services and thereby causes an outward shift in IS curve, as is shown in Fig. 20.6 where increase in Government expenditure leads to the shift in IS curve from IS1 to IS2.
Note that the horizontal distance between the two IS curves is equal to the increase in government expenditure times the government expenditure multiplier, that is, ΔG x 1/1-MPC which shows the increase in national income equal to the horizontal distance EK that occurs in Keynes’ multiplier model. However, in IS-LM model actual increase in national income is not equal to EK caused by the working of Keynesian multiplier.
This is because with the rightward shift in IS curve rate of interest also rises which causes reduction in private investment. It will be seen from Fig. 20.6 that, with the LM curve remaining unchanged, the new IS2 curve intersects LM curve at point B. Thus, in IS-LM model with the increase in Government expenditure (ΔG), the equilibrium moves from point E to B and with this the rate of interest rises from r1 to r2 and income level from Y1 to Y2.
Income equal to CK has been wiped out because of rise in interest causing a decline in private investment. Thus CK represents crowding-out effect of increase in government expenditure Thus, IS-LM model shows that expansionary fiscal policy of increase in Government expenditure raises both the level of income and rate of interest.

It is worth noting that in the IS-LM model increase in national income by Y1 Y2 in Fig. 20.6 is less than EK which would occur in Keynes’ model. This is because Keynes in his simple multiplier model assumes that investment is fixed and autonomous, whereas IS-LM model takes into account the fall in private investment due to the rise in interest rate that takes place with the increase in Government expenditure. That is, increase in Government expenditure crowds out some private investment.
Likewise, it can be illustrated that the reduction in Government expenditure will cause a leftward shift in the IS curve, and given the LM curve unchanged, will lead to the fall in both rate of interest and level of income. It should be noted that Government often cuts expenditure to control inflation in the economy.
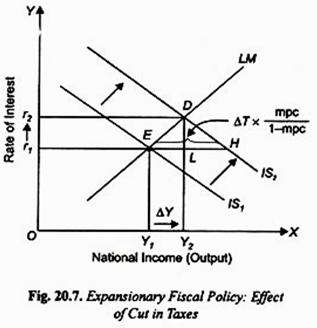
Expansionary Fiscal Policy: Reduction in Taxes:
An alternative measure of expansionary fiscal policy that may be adopted is the reduction in taxes which through increase in disposable income of the people raises consumption demand of the people. As a result, cut in taxes causes a shift in the IS curve to the right as is shown in Fig. 20.7 from IS1 to IS2.
It may however be noted that in the Keynesian multiplier model, the horizontal shift in the IS curve is determined by the value of tax multiplier times the reduction in taxes (ΔT), that is, ΔT x MPC/1-MPC and causes level of income to increase by EH.
However, in the IS-LM model, with the shift of the IS curve from IS1 to IS2 following the reduction in taxes, the economy moves from equilibrium point E to D and, as is evident from Fig. 20.7, rate of interest rises from r1 to r2 and level of income increases from Y1 to Y2. Income equal to LH has been wiped out because of crowding-out effect on private investment as a result of rise in interest rate.
On the other hand, if the Government intervenes in the economy to reduce inflationary pressures, it will raise the rates of personal taxes to reduce disposable income of the people. Rise in personal taxes will lead to the decrease in aggregate demand. Decrease in aggregate demand will help in controlling inflation. This case can also be shown by IS-LM curve model.
Through making appropriate changes in monetary policy the Government can influence the level of economic activity. Monetary policy may also be expansionary or contractionary depending on the prevailing economic situation.
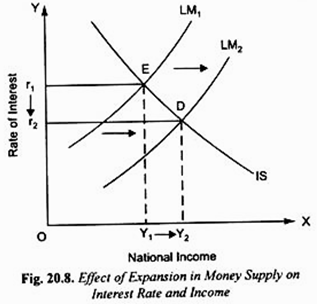
IS-LM model can be used to show the effect of expansionary and tight monetary policies . A change in money supply causes a shift in the LM curve; expansion in money supply shifts it to the right and decrease in money supply shifts it to the left.
Suppose the economy is in grip of recession, the Government (through its Central Bank) adopts the expansionary monetary policy to lift the economy out of recession. Thus, it takes measures to increase the money supply in the economy. The increase in money supply, state of liquidity preference or demand for money remaining unchanged, will lead to the fall in rate of interest.
At a lower interest there will be more investment by businessmen. More investment will cause aggregate demand and income to rise. This implies that with expansion in money supply LM curve will shift to the right as is shown in Fig. 20.8.
As a result, the economy will move from equilibrium point E to D and with this the rate of interest will fall from r1 to r2 and national income will increase from Y1 to Y2. Thus, IS-LM model shows that expansion in money supply lowers interest rate and raises income.
We have also indicated what is called monetary transmission mechanism, that is, how IS-LM curve model shows the expansion in money supply leads to the increase in aggregate demand for goods and services. We have thus seen that increase in money supply lowers the rate of interest which then stimulates more investment demand. Increase in investment demand through multiplier process leads to a greater increase in aggregate demand and national income.
If the economy suffers from inflation, the Government will like to check it. Then its Central Bank should adopt tight or contractionary monetary policy. To control inflation the Central Bank of a country can reduce money supply through open market operations by selling bonds or government securities in the open market and in return gets currency funds from those who buy the bonds. In this way liquidity in the banking system can be reduced.
To reduce money supply for fighting inflation the Central Bank can also raise cash reserve ratio of the banks. The higher cash reserve ratio implies that the banks have to keep more cash reserve with the Central Bank. As a result, the cash reserves with the banks fall which force them to contract credit. With this money supply in the economy declines.
Thus, IS-LM model can be used to show that reduction in money supply will cause a leftward shift in LM curve and will lead to the rise in interest rate and fall in the level of income. The rise in interest rate which will cause reduction in investment demand and consumption demand and help in controlling inflation. This is shown in Fig. 20.9.